Not for birds in Africa, apparently — and surprisingly, at least to me. 1 A recent paper looked at likely turnover of species in Important Bird Areas (IBAs) in Africa under a range of climate change scenarios. The results showed that although there would be significant shifts in the species composition of individual IBAs, overall about 90% of 815 endangered species “are projected to retain suitable habitat by 2085 in at least one IBA where they occur currently.” And some IBAs will become newly suitable for some species. Only a few endangered species will lose all suitable habitat from the IBA network.
Nevertheless, the authors acknowledge the importance of the shifts in species distribution and suggest a number of recommendations. In particular, the results highlight the need for regionally focused management approaches. For example, increasing the number and size of protected areas, providing ‘stepping stones’ between habitats and protected areas and restoring critical types of habitat, as well as ensuring that the current IBA network is adequately protected into the future.
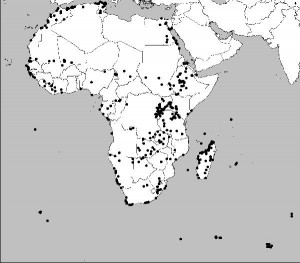
Sensible recommendations, which would apply all the more strongly to any similar network for crops wild relatives, say, which don’t by and large have the mobility of birds. 2 We need to carry out a similar resilience study for CWRs in protected areas, I would suggest. But also, do we know how good the IBAs are at capturing CWR diversity? I suspect when people look at CWR distributions in protected areas, it is mainly national parks and the like that they consider, rather than such specialized things as IBAs, but I could be wrong. 3 Here’s the distribution of IBAs in Africa. I seem to be having a thing about maps of Africa lately.
- It’s been a week for surprises. A meta-analysis also just out suggested that “recovery is possible and can be rapid for many ecosystems, giving much hope for humankind to transition to sustainable management of global ecosystems.” But that’s another story.
- Ok, maybe the ones which are bird-dispersed do! And the ones which don’t move around so well could be helped out, of course, although the most recent paper on such “assisted migration” is definitely in the “no” camp.
- And Nigel and Shelagh will quickly tell me if I am, no doubt.
I agree with the points you raise. Maybe what is required is a more dynamic approach to CWR conservation. One that links up protected areas (and other specialised conservation areas) much more fluidly with conservation outside these areas. More collaboration with the ‘corridors’ people and somehow involving local communities in fostering wild relatives. Instead of thinking of conservation inside and outside protected areas as two separate entities. Then embedding ex situ conservation in this so that it mops up those wild relatives that are especially vulenrable, endangered or have poor mobility (possibly a role for the Millenium Seed Bank collaborating with the traditional crop genebanks here). A more holistic approach to increasingly mobile target areas. More complexity to an already challenging subject!